Arthropods are the largest category of animals, accounting for approximately 85% of the more than 1 million species of animals currently known. The body of this phylum is divided into three parts: head, thorax and abdomen, and the appendages are segmented, hence the name arthropods. Currently, a total of 4,362 species of arthropods have been recorded in the China Sea, accounting for approximately 1/2 of all marine species in the China Sea.
There are four major categories of arthropods in the ocean: Myelostomata, Sea Spiders, Insecta and Crustacea. Among them, Crustacea is a very important group of marine organisms. The shrimps and crabs we usually like to eat belong to this class. type.

Hainan's top three crabs

Chinese New Point Crab

Grate-fronted crab

Tu's fiddler crab
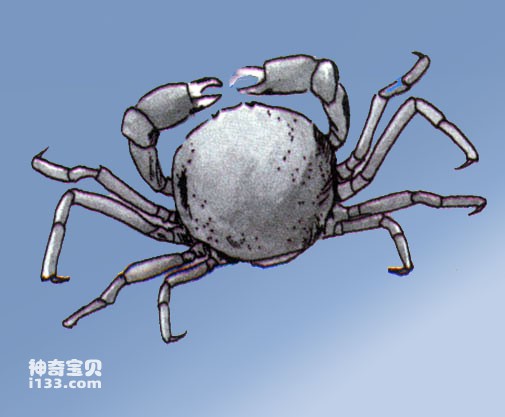

Bean light crab

long-winged crab

fiddler crab
Fiddler crab. The body is dark brown with red feet. One claw of a male crab is very large, accounting for about half of the total weight; the other half is smaller than the legs. Both claws of female crabs are small and equal in size. Fiddler crabs burrow in groups on beaches and feed on soil containing organic debris. At low tide, you can often see many strange crabs running around in the harbor and on the mudflats of the estuary, very busy and active. They run and forage on the mudflats when the tide is low, and quickly burrow into caves when the tide is high. The activities of this kind of crab are closely related to the rising and falling tides of the sea water, hence the name "tide fetching" or "tide watching".
People know that ocean tides are mainly caused by the gravity of the moon, and the height of the tides is also affected by the gravity of the sun. It seems that fiddler crabs can calibrate their "clocks" according to both the sun and the moon. They change color according to the solar day, and at the same time they rise and fall with the tides, that is, they search for food according to the lunar day. They will be safely hiding in their caves 10 minutes before they feel the tide is coming. They eat in the same month.

Chinese shrimp
Chinese prawn, also known as Oriental prawn. It lives on the bottom of shallow seas and often crawls on the sand. It lurks in the sand during the day and is active in the middle and upper layers of the sea at night. It feeds on benthic shrimps, small crustaceans and bivalve molluscs, as well as the larvae of various other invertebrates. It also eats diatoms. It is distributed along the coast of my country, but mainly in the Yellow Sea, Bohai Sea and the western coast of North Korea.

The crab that is good at camouflage--Guan Gong Crab
Crabs living in the ocean are a very prosperous branch of the crab family. Not only do they have many types, but they also have different abilities. There are sand crabs that walk like flying, hermit crabs that don’t pay rent, coconut crabs that can climb trees, and tall crabs that use their one-meter-long legs to support themselves and crawl on the seabed, etc. Among the many types of sea crabs, the most peculiar and legendary is the Guan Gong crab.
The Guan Gong crab is a small crab that lives on the muddy and sandy bottom of shallow seas and lives on the bottom. Its carapace is only about 3 centimeters wide, the distance between its back and abdomen is very small, and there is almost no thickness, so the crab body looks special. Thin. Because the grooves on its carapace resemble the facial makeup of Guan Gong, the general of the Shu Kingdom during the Three Kingdoms period in ancient China - lying silkworm eyebrows and red phoenix eyes, it is called Guan Gong Crab in our country.
This small sea crab has four pairs of steps. The last two pairs of steps are short, sharp and scissor-shaped. The Guan Gong crab can use these two pairs of short steps to grab shells, stones or leaves that are larger than its own body. Carrying other objects on its back, it camouflages its body to defend itself from enemies.
The name of this small sea crab in Japan is Heike crab. Why do the Japanese call it Heike crab? There is another allusion here. The Taira family was originally a famous samurai family in Japan. In 1185, they fought with the Genji family at Tannoura in the Oto Inland Sea and were defeated by the Genji. The Taira clan samurai were buried in the sea. The Japanese believe that this crab is the incarnation of the undead souls of the Heike samurai, because the grooves on its carapace resemble the face of an angry man: its eyes are raised, its mouth is formed into a figure eight, and it looks like it carries a lot of hatred. , and because they mostly live in the Inland Sea, the Japanese call it Heike crab. The legend about the Heike crab is still widely circulated in Japan. Even Japanese natural science books call this crab the Heike crab.
In 1985, it was the 800th anniversary of the tragic defeat of the Heike clan samurai in the Battle of Honoura. Japan's "Asahi Shimbun" published some reports and debates about this crab specifically for this purpose. The content of the debate was why the Heike crab was so special in the Inland Sea. many. American Carl Sager believes that after Japanese fishermen caught this crab, they thought it was the soul of the Taira samurai, so they released them into the sea again, thus promoting the large-scale reproduction of this crab. Dr. Tsune Sakai of Yokohama University in Japan believes that this explanation cannot be used, because the Heike crab does not only live in Tannoura. The reason why this kind of crabs are able to reproduce in large numbers is mainly because they don't have much meat at all and are not edible at all. It is not due to any undead reasons. Obviously what Hisashi Sakai said makes sense.
Hermit crabs are cold-water species and are the dominant species in the deeper seabed of the Yellow Sea.

hermit crab
Distributed in the waters of my country’s Paracel Islands
Checkered claw crab

Spotted crabs are distributed in the South my country Sea and cohabitate with sea urchins

Rock shrimp, also known as shore shrimp, is distributed in tropical waters such as the South China Sea in my country.

lobster
Lobster is only produced in the southern part of the East China Sea and the South China Sea in my country; the shallow seas in the east and west of Guangdong Province have greater production.
The living fossil among swimming crab arthropods - horseshoe crab
The horseshoe crab is a sea-dwelling arthropod that uses gills to breathe. Because its appendages are located around the mouth, it belongs to the class Limulus. The body of Tang is scoop-shaped and consists of three parts: head, chest, abdomen and tail sword. The entire body is covered with hard armor, with a rounded back and a sunken abdomen. In the animal kingdom, it is rare for horseshoe crabs to stubbornly maintain their ancient appearance and refuse to evolve for more than 400 million years. This is a great advantage for people today to study the evolution of organisms hundreds of millions of years ago.

Lobster, swimming crab, living fossil among arthropods - horseshoe crab
The ancestor of the horseshoe crab first appeared in the Devonian Period of the Paleozoic Era and occupied a dominant position. At that time, dinosaurs had not yet risen, and primitive fish had just appeared. As time went by, some animals of its contemporaries either evolved or became extinct. Only the horseshoe crab survived and still retained its original and ancient appearance, becoming Nowadays, people study the evidence of paleontological fossils, so horseshoe crabs are called "living fossils". Judging from its embryogenesis process, the young horseshoe crab resembles the trilobites that appeared in the Cambrian period of the Paleozoic Era, so horseshoe crabs may have evolved from a common ancestor with trilobites.
For hundreds of millions of years, horseshoe crabs have grown, developed, and reproduced in obscurity. For a long time, people only used it as a kind of seafood to taste the deliciousness of its meat and eggs, and had no other use. However, by the early 1960s, it was discovered that the eyes of horseshoe crabs are much like geomagnetic wave receptors and can accurately capture food on the dimly lit seabed. Therefore, horseshoe crab eyes have become the target of bionics. Based on the structural principles of horseshoe crab eyes, people developed and designed many new instruments. At this point, this unknown ancient animal suddenly became famous.Noisy, attracted the attention of the world.

Horseshoe crab on the beach
The round-tailed horseshoe crab is the smallest of the existing species. Its average body length is about 30 cm, and its average weight is about 0.5 kg. According to past data, there is only one species of Chinese horseshoe crab along the coast of my country. In 1984, during the investigation of horseshoe crab resources along my country's coast, scientific workers from the Guangxi Institute of Oceanography discovered round-tailed horseshoe crabs in the shallow waters along the Beibu Gulf of the South China Sea. For this reason, there are currently two types of horseshoe crabs: Chinese horseshoe crab and round-tailed horseshoe crab along the coast of my country.
The meat of the horseshoe crab is inedible and can cause poisoning or even death after people eat it. Therefore, fishermen along the coast of Guangxi call it ghost horseshoe crab.
The first discovery of the round-tailed horseshoe crab along the coast of Beibu Gulf in my country is undoubtedly very important and gratifying. This not only enriches the species of horseshoe crabs along my country's coast, but also provides conditions and possibilities for further research on its morphology, ecology and physiological functions.
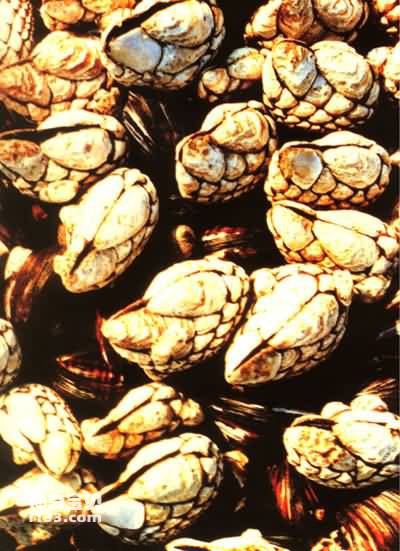

barnacles
When we walk on the beach, we will also see clusters of gray-white small animals with calcareous shells on the rocks. These small animals are another branch of the large family of arthropods, called barnacles. The shape of a barnacle is a bit like a horse's tooth, so people living by the sea often call it "horse's tooth". Barnacles are not only attached to the rocks, but also fixed to the hull, and cannot be washed away by rough waves. Why can they be firmly attached to rocks and ship hulls? This is because every time a barnacle sheds its skin, it releases a layer of sticky barnacle primary glue, which contains a variety of biochemical ingredients and extremely strong adhesion. At present, barnacles' strange sticking ability has attracted people's attention. Once successfully developed, this "barnacle adhesive" will show its power in underwater rescue and leak repair work.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.