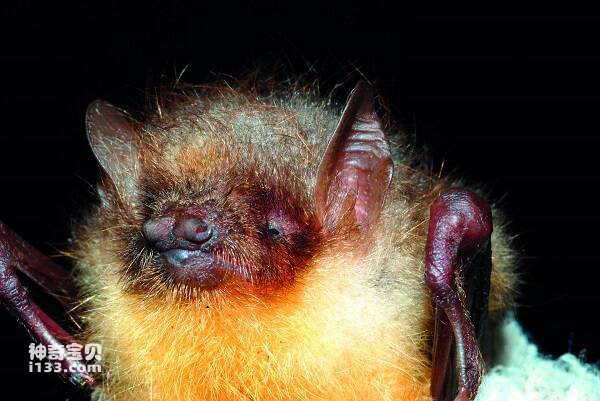
Myotis ricketti
IUCN
LCBasic Information
Scientific classification
- name:Myotis ricketti
- Scientific Name:Myotis ricketti
- Outline:Chiroptera
- Family:Chiroptera Batidae Myotis
Vital signs
- length:60-65mm
- Weight:20-30g
- lifetime:
Feature
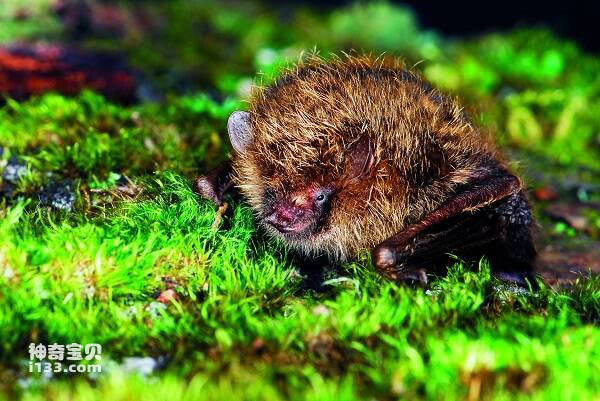
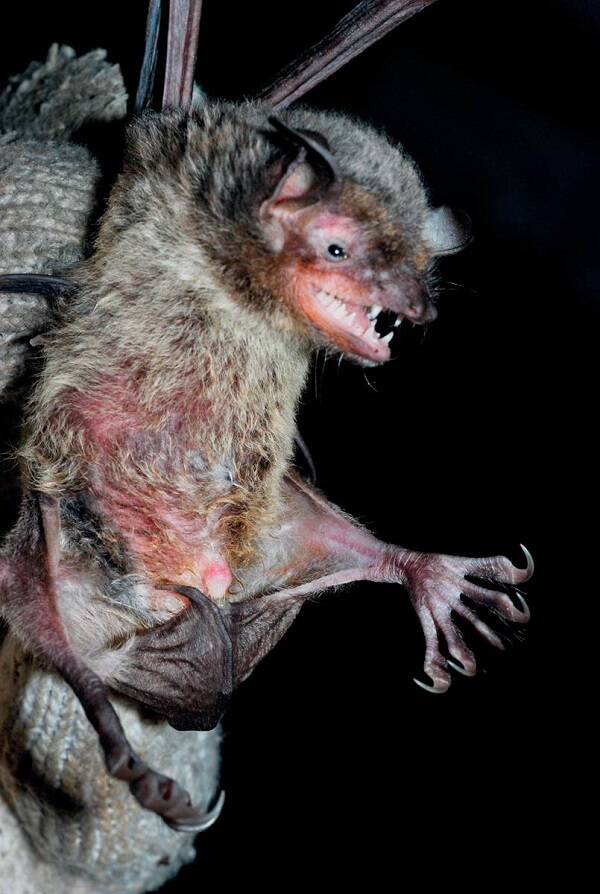
The hind feet are large and several tibia length, the claws are strong and curved, and the backs of the feet have stiff hairs.
Distribution and Habitat
It is distributed in Fujian, Anhui, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shandong, Shanxi, Yunnan, Guangdong, Sichuan, Macau and Hong Kong. It is distributed abroad in Laos and Vietnam.
The bat lives in large dark, damp caves. Groups of dozens or hundreds are often gathered, which can be seen in the same cave as the Chinese Myotis bat and other bat species.
Appearance
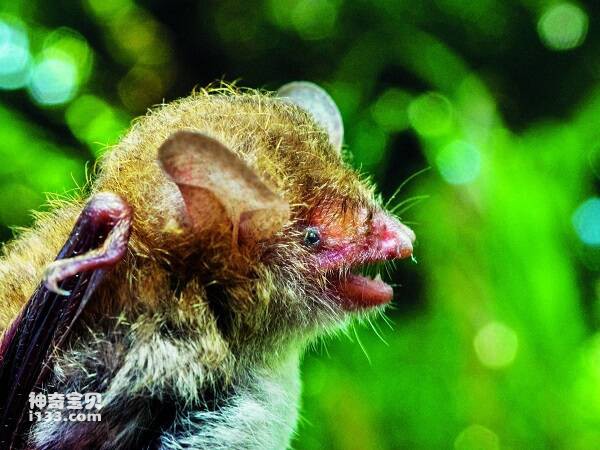
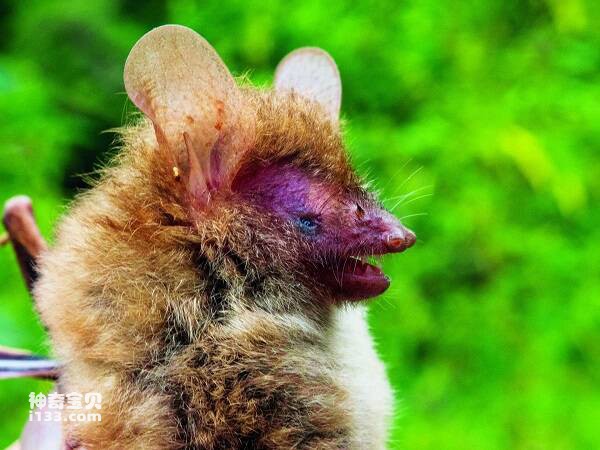
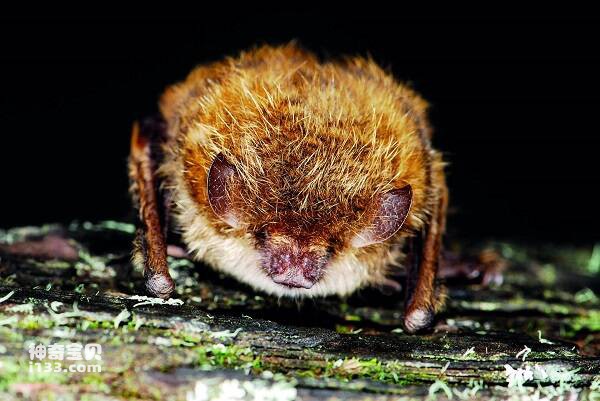
A little larger and stronger. Forearm length 54-61mm. The ears are short, the front fold does not reach the rostral end; The tragus is short, slightly pointed at the end, less than half the length of the ear. The alar membrane ends at the middle or base of the tibia. The hind foot is large and has sharp claws, which are almost as long as the shin; Long distance. The caudal terminal segment of the caudal vertebra protrudes from the posterior margin of the interfemoral membrane. The body hair is short and fluffy. The upper body hair is light brown gray, the lower body is gray white, and albino individuals have been collected.
Details
Big-footed mouse-eared bats have attracted much attention because of their special habit of catching fish on the surface for food. Often clustered in hills or mountains, caves. Estrus in late autumn and early winter, and 1 baby in June of the following year. The adult body weight is generally 20g-30g, the head length is 60mm-65mm, it is a kind of large mouse-eared bat. The most typical morphological feature is the unusually developed hind foot, about 20mm long, which is twice the length of the hind foot of other insect-eating myotis bats, and the hind foot is very sharp, like a fish hook.
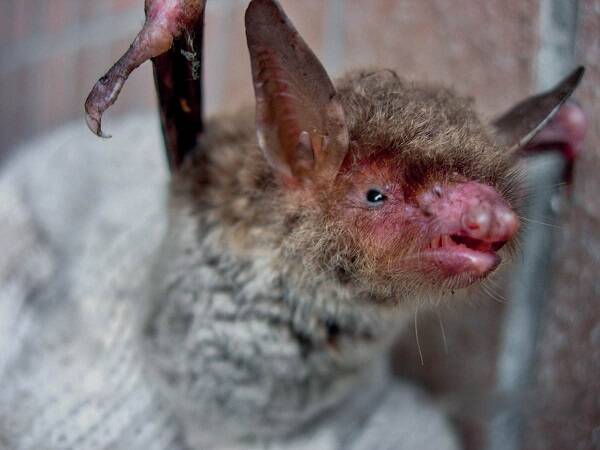

The Great footed mouse-eared bat is another fish-eating bat discovered after the Mexican rabbit-lipped bat, the Southern rabbit-lipped bat and the Sonora Mouse-eared bat, and is the first fish-eating bat found in China. This is the first time in Asia and the third time in the world. The discovery of fish-eating characteristics is of great scientific significance, as it once again confirms that a particular type of animal lifestyle can originate independently in different regions. They are rare in number and should be protected by relevant authorities.
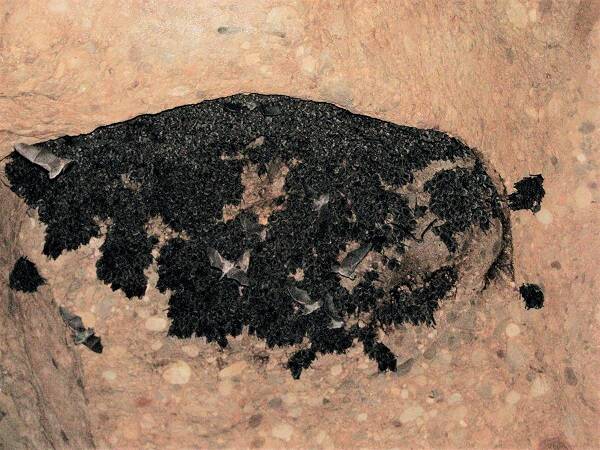

The bat has no seasonal migration habit, and often lives in clusters in hills or mountains, caves and crevices in city walls. It is mainly distributed in southeast China, including parts of Fujian, Guangxi, Zhejiang, Hong Kong, Shandong, Shaanxi, Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangxi and Yunnan, and is rare in Beijing.
The big-footed bat will use Trawling hunting behavior on the water surface, which is the same behavior as fishing bats abroad. Its surface hunting has to do with the signature of their echolocation signal. The echolocation signals of Myotis macropoda belong to the FM type with short sweep time and low main frequency.
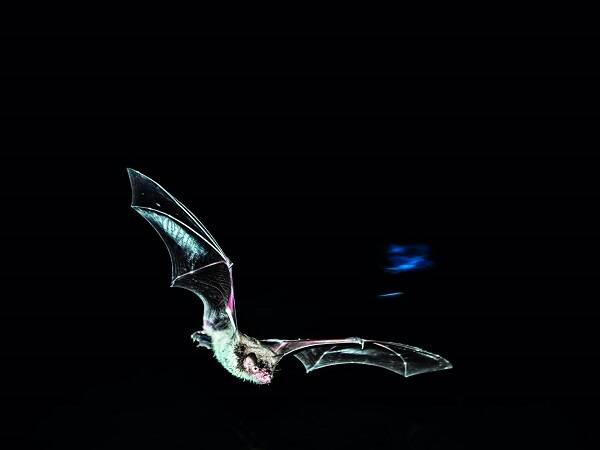

This call is suitable for hunting in an open environment with low background noise. If big-footed mouse-eared bats hunt insects near the ground in a meadow, the background echoes mask those reflected by prey, creating a background interference effect. The bat cannot pick up accurate information about its prey from the echoes, so it cannot determine the exact location of its prey. The relatively "calm" water is much less noisy for the big-footed bat.
Big-footed Myoetis bats in Beijing mainly eat three kinds of fish, including carassius auratus seeds (fish). These broad-finned bats swim and even jump out of the water, so their exposed bodies reflect ultrasound more effectively than the surface of the water
It has been included in the Chinese Red List of Biodiversity - Vertebrate volume, and the assessment level is near threatened NT.