Exotic
Exotic、ExoticShorthair,Exotic shorthair cat, Exotic shorthair cat, Shorthair Persian cat, Exotic shorthair
Exotic Shorthair, also known as Exotic or ExoticShorthair, was bred in the 1···

Tigertight Felis
Tigertight Felis,Syrian marble cat, tiger cat
The scientific name of the tabby cat is Tigertight Felis, which was bred by ···

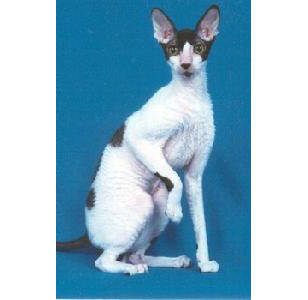
American Wirehair
American Wirehair,American Wirehair
The American Wirehair cat is called American Wirehair in foreign language. I···

Felis nigripes
Black-footed cat,Small tabby cat
The black-footed cat (Felis nigripes), named for the black markings on the s···

Felis margarita
Felis margarita,Sand Cat、Sand Dune Cat,Chat des sables,Gato de las Arenas、Gato del Sahara, ArabicQit al rimal, pshaya koshka,sand cat, desert cat
The Sand Dune Cat (scientific name: Felis margarita) is known as Sand Cat, S···

Cheetah
Acinonyx jubatus
Cheetah (scientific name: Acinonyx jubatus) English Cheetah, Hunting Leopard···

Enhydra lutris
Enhydra lutris,Sea Otter
Sea Otter (scientific name: Enhydra lutris) is also known as Sea Otter in fo···

Aonyxcapensiscongica
Aonyxcapensiscongica,Congo small-clawed otter, Cameroon clawless otter
The Zaire small-clawed otter is also known as the Congo small-clawed otter (···

Pteronura brasiliensis
Pteronura brasiliensis,Giant Otter,giant otter, giant otter, South American giant otter, Brazilian giant otter
Giant Otter (scientific name: Pteronura brasiliensis) is also known as Giant···

Lontra felina
Lontra felina,chungungo、Marine Otter,Cat
Peruvian Otter (scientific name: Lontra felina) is also known as chungungo a···

Lontra longicaudis
Lontra longicaudis,Long-tailed otter
Long-tailed Otter (Lontra longicaudis) They seem to prefer clear rivers and ···

Lontra provocax
Lontra provocax
The Chilean otter (scientific name: Lontra provocax) is a semi-aquatic mamma···

Lontra canadensis
Lontra canadensis,North American River Otter,Canadian otter, northern otter
North American River Otter (scientific name: Lontra canadensis) is also know···

Lutra sumatrana
Lutra sumatrana,Hairy-nosed Otter,Sumatran otter
Hairy-nosed Otter (Lutra sumatrana), also known as Hairy-nosed Otter, lives ···

Lutra nippon
Lutra nippon
The Japanese otter, scientifically known as Lutra nippon, is endemic to Japa···

Taxidea taxus
Taxidea taxus,American Badger,Badger
American Badger (scientific name: Taxidea taxus) is also known as American B···

Mellivora capensis
Mellivora capensis, Honey Badger、 Ratel, Blaireau à miel, Ratel, Honigdachs,Flathead
Honey badger (scientific name: Mellivora capensis) English Honey Badger, Rat···

Mydaus javanensis
Mydaus javanensis,Indonesian stink badger, Sunda stink badger
The Sunda stink badger (Mydaus javanensis), also known as the Indonesian sti···